What is the FCB Grid? Definition, Model, and Applications in Advertising
One-Sentence Definition
The FCB Grid is an advertising strategy framework that classifies products and services according to the level of consumer involvement (high vs. low) and the dominant decision process (thinking vs. feeling), helping marketers craft more effective, targeted campaigns.
Detailed Explanation
Introduced by Richard Vaughn in 1980, the FCB Grid (Foote, Cone & Belding Model) provides a simple yet powerful 2x2 matrix to guide advertising decisions based on consumer psychology (b-plannow.com). The two axes are:
- Vertical Axis: Involvement — High or Low (how important or risky the purchase is for the customer)
- Horizontal Axis: Processing — Thinking (rational, logical) or Feeling (emotional, intuitive)
Mapping a product or brand onto this grid determines the optimal messaging style and advertising channels. The approach helps advertisers avoid one-size-fits-all messaging and adapt campaigns to real consumer motivations.
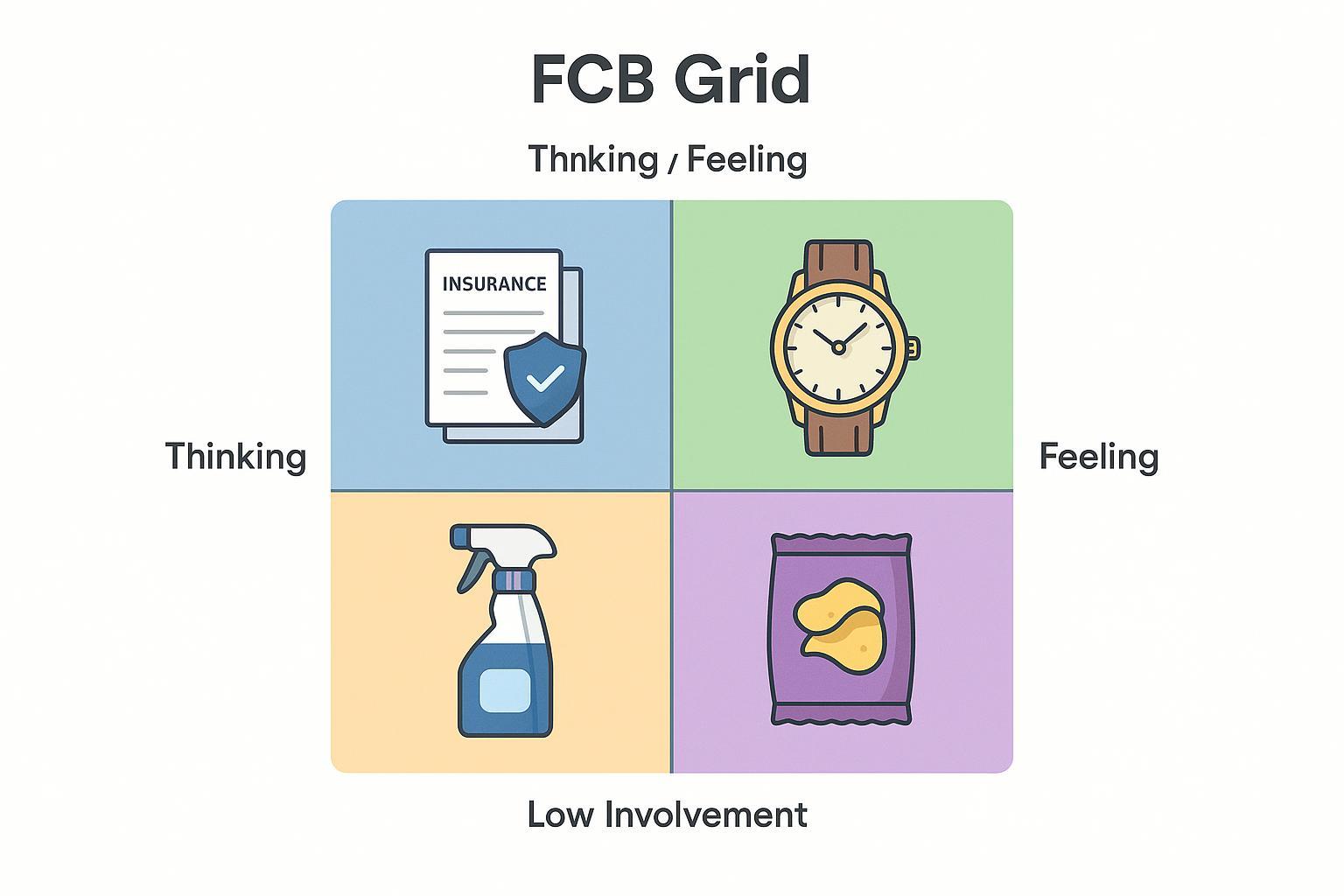
Key Components: The Four Quadrants
- High Involvement, Thinking
- Typical Products: Life insurance, cars, mortgages
- Campaign Strategy: Provide detailed, rational information—whitepapers, webinars, in-depth web content
- Digital Example: Interactive financial planning tools, long-form blog guides
- High Involvement, Feeling
- Typical Products: Luxury watches, designer fashion, weddings
- Campaign Strategy: Evoke aspiration and emotion—storytelling videos, influencer campaigns
- Digital Example: Emotional storytelling via YouTube ads, Instagram influencer narratives
- Low Involvement, Thinking
- Typical Products: Household cleaners, personal care basics
- Campaign Strategy: Focus on convenience and habit—reminder ads, coupons, shelf placement
- Digital Example: Retargeted banners, one-click Amazon promotions
- Low Involvement, Feeling
- Typical Products: Snacks, soft drinks, fast food
- Campaign Strategy: Maximize fun and enjoyment—sensory cues, lifestyle visuals
- Digital Example: Social media memes, viral short-form videos
How to Use the FCB Grid: Practical Steps
- Assess Involvement: Is the product purchase routine or important? High involvement usually means personal risk or high cost.
- Determine Decision Basis: Are customers motivated by logic (features/benefits) or by connection (brand, values, self-expression)?
- Map to Quadrant: Use customer data, surveys, and competitor analysis to place the product.
- Choose Messaging Style: Match content and tone to the quadrant (informational vs. emotional, rational vs. sensory).
- Select Channels: Long-form content and webinars (high involvement) versus quick, visual, or experiential media (low involvement).
- Measure and Iterate: Consumer perceptions can evolve; review campaign performance and adjust as needed.
Real-World Mini-Case Examples
- High Involvement/Thinking: A bank launches a series of webinars and blog articles demystifying mortgage options, supported by detailed calculators.
- High Involvement/Feeling: A luxury auto brand uses influencer storytelling backed by cinematic social ads to launch its latest sports car.
- Low Involvement/Thinking: A detergent brand runs recurring banner ads on shopping apps highlighting savings and convenience.
- Low Involvement/Feeling: A chip company sparks a trend with shareable TikTok challenges centered on snacking enjoyment.
Related Concepts and Comparison
- AIDA Model: Outlines Attention-Interest-Desire-Action sequence. Focuses on consumer journey steps, while the FCB Grid emphasizes message style by product type.
- Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM): Explains how people process messages centrally (thinking) or peripherally (feeling)—the psychological root of the FCB Grid’s axes.
- BCG Matrix: Maps product lines by growth and market share—useful for portfolio decisions, not messaging.
- Perceptual Mapping: Visualizes brand positions in consumer minds, whereas the FCB Grid helps design communication logic. For a more detailed discussion, see this comparison resource.
Adapting the FCB Grid Today
Today’s marketers use the FCB Grid for both traditional and digital campaigns, leveraging AI and analytics to refine targeting. Its principal value is in forcing teams to define what drives customer choices—and to adapt creative strategy accordingly. Note, however, that products and consumers can move between quadrants over time, especially in fast-changing or hybrid-value markets.
Limitations
While widely used, the FCB Grid can sometimes oversimplify complex buying processes. Some products cross quadrants, or consumer motivations may shift rapidly—so always combine with ongoing research and segmentation.
References:
- b-plannow.com—Understanding Consumer Behavior for Effective Communication Strategies
- theinvestorsbook.com—FCB Grid Meaning, Definition, Components, Example
- Vaughn, R. (1980). How Advertising Works: A Planning Model. Journal of Advertising Research.

