Prompt Chaining in 2024: Unlocking Step-by-Step AI for Content Marketing, SaaS, and Blogging Platforms
Have you ever tried to get an AI to write a truly great blog post or automate a complex marketing task, only to end up with something robotic or shallow? If so, you’re not alone. The secret sauce behind smarter, stepwise AI workflows—especially in 2024’s crowded landscape of SaaS and automated content platforms—is a technique called prompt chaining. But what does this mean, why is it powerful, and how can it work for you?
What Is Prompt Chaining? (Simple Explanation)
Prompt chaining is an AI technique where a large or complex goal is broken down into a series of smaller, manageable steps. Each step is handled by its own AI prompt, and the output from one becomes the input for the next—like runners passing a baton in a relay race. The chain guides the AI logically and incrementally until you get a polished, detailed result.
In other words: instead of telling an AI “Write me a perfect blog post on climate marketing,” prompt chaining lets you say, “First, find the best keywords. Next, outline the main points. Then, write each section. Finally, optimize everything for SEO and brand voice.” Each step gets its own prompt, and the AI walks through them in sequence.
Why Use Prompt Chaining? (The Relay Race Analogy)
Think of prompt chaining as an assembly line or a relay race:
- Each worker (or runner) has a specialized job.
- The baton (output) is handed smoothly from one to the next.
- At the end, you get a refined product—far better than asking one person to do everything all at once.
AI works much the same way; chaining prompts helps the model stay organized, thorough, and less likely to get confused or skip important details.
How Is Prompt Chaining Different? Comparison Table
| Concept | Definition | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt chaining | Multiple, sequential prompts; output from each feeds into the next step | Modular workflow, step-by-step |
| Chain-of-thought | Single prompt asking AI to reason step-by-step within one answer (no multi-stage relay) | One big prompt, not multiple prompts |
| Prompt sequencing | Ordered prompts, but output-input linkage isn’t required | Steps may be unrelated, less integrated |
Sources: Prompt Engineering Guide, PromptHub, TechTarget
How Prompt Chaining Works (Stepwise Walkthrough)
Let’s take a real example for marketers or AI content creators:
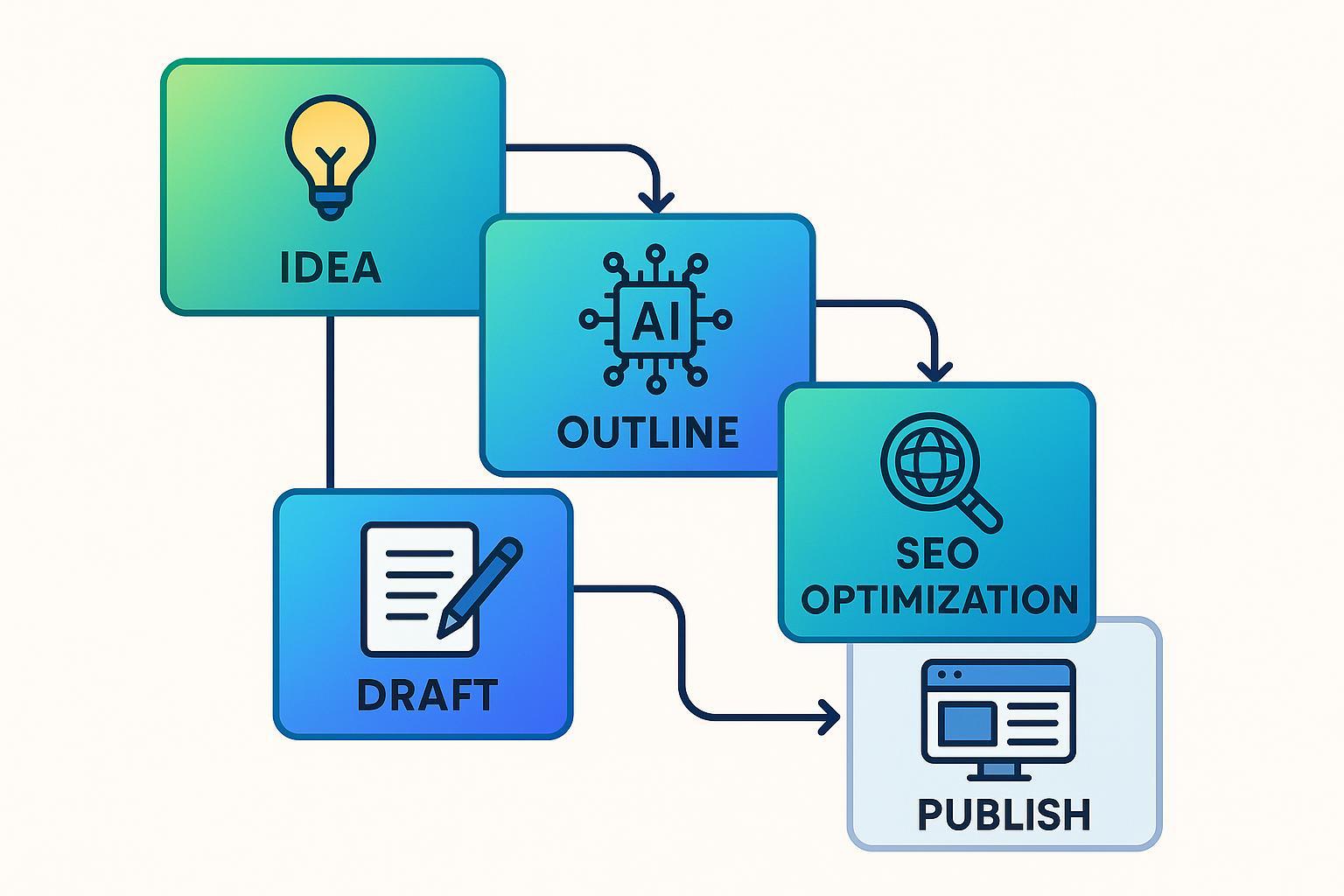
Blog Post Creation via Prompt Chaining
- Start With the Core Idea
"Give me trending blog topics in eco-friendly home decor." - Generate an Outline
Feed the best topic from above into: “Create a detailed outline.” - Draft Each Section
Give the outline to: “Draft a 200-word introduction.” Repeat for each section. - SEO and Tone Enhancement
Pass the draft to: “Enrich this with SEO keywords and match my brand’s tone.” - Finalize and Review
Prompt for a summary, fact-checks, or calls to action.
Each link in the chain builds on the last, ensuring nothing gets lost or half-finished. This approach is the backbone of many AI blogging and marketing automation platforms.
Real-World Applications: Content Marketing, SaaS, AI Blogging
Content Marketing:
- Keyword research → Outline → Draft → SEO optimization → Social repurposing (as outlined in DataCamp’s tutorial).
SaaS Workflows:
- AI triages support tickets: extract topic → classify urgency → suggest solutions → escalate as needed.
- Product feedback analysis: group comments → summarize pain points → generate action items.
AI Blogging Platforms:
- From ideation to outline, to section-by-section drafting, to SEO checks, to multi-platform adaptation—all via prompt chaining.
Going Deeper: Branching, Conditional, and Iterative Chains
Advanced AI workflows in 2024 often use:
- Branching: Forks in the chain (e.g., generate separate content for Facebook and LinkedIn after a single analysis prompt)
- Conditional Chains: Steps depend on previous results (if customer sentiment is negative, prompt to write a custom apology email)
- Iterative Loops: Repeat a step until it meets a certain quality (“Revise blog headline until 8/10 creativity score”)
Frameworks like LangChain and DSPy are rapidly making these patterns more accessible.
Benefits and Limitations (Truth Table)
| Aspect | Benefit | Limitation/Challenge | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Output Quality | Finer control, focus, incremental improvement | Errors can “multiply” in the chain | Add checks, review |
| Workflow Clarity | Step-by-step review and debugging possible | May feel slower/more steps | Automate reuse, nest |
| Adaptability | Easy to swap, skip, or re-order steps | Complex chains can become unwieldy | Visual editors, frameworks |
| AI Context Limits | Helps manage longer, chunked tasks | AI models still have length/context limits | Summarize, split chains |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Do I need to code to use prompt chaining?
No—many SaaS and content platforms now offer drag-and-drop or template-based chaining.
2. Can I use prompt chaining for things other than writing?
Absolutely! Marketers use it for campaign planning, research, social automation, product onboarding, and more.
3. What’s the main risk?
Error propagation: mistakes early in the chain can snowball. Always test and validate each step.
4. How does it differ from old-school workflow automation?
Prompt chaining harnesses generative AI’s reasoning—not just rigid logic or predefined forms. It’s more flexible for knowledge and language tasks.
5. What are the hottest trends in 2024?
- Multimodal chaining: Connecting tasks across text, images, and even video.
- Agentic workflows: Multiple AI “agents” collaborating in chains, not just single prompt streams.
- Native support in SaaS: Marketers can now build prompt chains directly in leading platforms—no custom scripting needed.
Business-Friendly Analogy: The Relay Race
Each step is like a sprinter running just their part of the race—focused, specialized, and passing the baton smoothly. Instead of relying on a single overworked runner (one big prompt), a team (prompt chain) shares the load for a faster, more reliable win.
Glossary
- Prompt: The instruction or input you give an AI for a specific task ("Write a catchy blog headline.")
- Prompt Chaining: Linking several AI prompts together so each step helps build a complex result
- Chain-of-Thought: Reasoning steps built inside a single prompt/response, not across multiple prompts
- LLM (Large Language Model): Type of AI trained on massive text data, like GPT-4 or Claude 3
- Workflow Automation: Using tools (including AI) to make business processes run without manual effort
Getting Started: Tips for Marketers, SaaS Teams, and AI Content Creators
- Start simple: Break your process into steps, and try chaining them in your favorite AI or content tool
- Use visual workflow builders (found in leading AI blogging and marketing SaaS)
- Test each chain step for quality before moving to the next—don’t be afraid to refine or reorder
- Stay tuned for new features: platforms like LangChain and others are redefining workflow automation weekly
- Check Prompting Guide for technique deep-dives
Future Directions: Where Prompt Chaining Is Headed (2024 and Beyond)
- AI is rapidly evolving to chain prompts not just across text, but also images, video, and even real-time data streams (“multimodal”).
- Agentic chaining—where AI “agents” can coordinate, delegate, and adapt—will soon unlock new forms of workflow automation (Orq.ai).
- Expect wider adoption of chaining frameworks, especially inside SaaS/content platforms, making advanced chains accessible to non-coders.
Actionable Summary
Prompt chaining is shaping the way forward for smarter, more reliable AI workflows—especially in content marketing, SaaS, and blogging. By breaking tasks into focused steps and handing off smoothly between them, you regain control and creativity at every stage. The future? Even more power, flexibility, and automation at your fingertips—no Ph.D. required.
Want to explore more? Dive into expert guides and examples here:
- Prompt Engineering Guide: Prompt Chaining
- PromptHub’s Prompt Chaining Guide
- DataCamp Tutorial: What Is Prompt Chaining?
Article last updated: June 2024.

