How to Defend Against MFA Bypass: Practical Strategies to Prevent MFA Avoidance Tactics in 2025
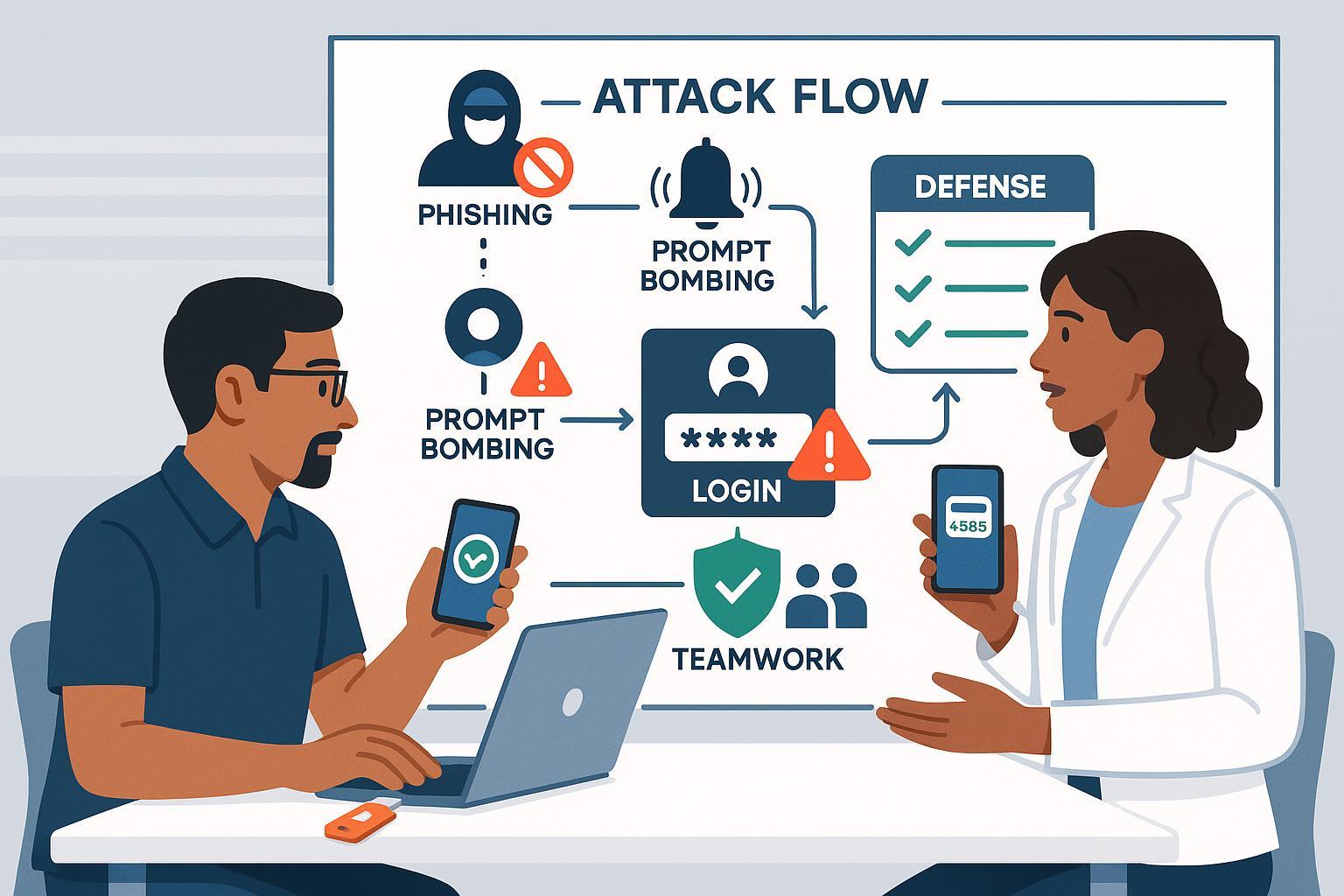
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is no longer optional in 2025—but attackers are getting smarter at bypassing it. This guide is your complete playbook for preventing, detecting, and responding to the latest MFA avoidance and bypass attacks, with practical steps for IT teams, business leaders, and everyday users.
What You’ll Achieve
- Detect and prevent 2025’s most advanced MFA bypass attacks (prompt bombing, adversary-in-the-middle phishing, session hijacking, social engineering)
- Choose and deploy phishing-resistant MFA solutions
- Harden your identity provider (IdP) settings (Microsoft 365, Okta, Google Workspace, AWS)
- Train users to recognize attacks and report suspicious activity
- Respond quickly and effectively if your MFA is bypassed
Time estimate: 90 minutes for full business prep; 10–30 minutes per platform/user setup.
Who Should Use This Guide?
- IT Administrators securing organizational access and configuring MFA policies
- Business Owners & Managers making security decisions for teams
- All Users & Employees responsible for protecting their accounts
Quick Prep: Role-Specific MFA Defense Checklist (2025)
IT/Admin
- [ ] Enforce phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/WebAuthn hardware keys or passkeys)
- [ ] Disable SMS- and email-based second factors wherever possible
- [ ] Limit push notification prompts; enable number matching on authenticator apps
- [ ] Configure adaptive/risk-based authentication and monitor login patterns
- [ ] Regularly audit MFA logs and anomalous sign-ins
- [ ] Update legacy protocol and disable outdated authentication flows
- [ ] Implement automated session monitoring/revocation
Business Owner/Manager
- [ ] Verify all critical apps/platforms use modern (phishing-resistant) MFA
- [ ] Schedule quarterly training and phishing simulation exercises for staff
- [ ] Document incident response/escalation procedures for MFA issues
- [ ] Allocate budget for hardware keys or advanced security apps
- [ ] Ensure helpdesk staff are trained to recognize/report MFA bypass signals
End User/Employee
- [ ] Use hardware security keys or mobile authenticators (never SMS codes if you can help it)
- [ ] Never approve repeated, unexpected MFA requests (“prompt bombing”)
- [ ] Report any suspicious login or authentication events to IT/security
- [ ] Don’t share codes or approve requests after phone support calls—verify every channel
- [ ] Take part in security training and simulations
(Printable/downloadable checklist: CISA MFA Quick Guide — see official CISA resources for details)
Step-by-Step: How to Block and Counter MFA Bypass Tactics
1. Understand Today’s MFA Bypass Threats (2025)
Read up on the primary attack strategies:
- Prompt Bombing/Fatigue Attacks: Surge of push/auth requests designed to wear users down
- Counter: Enable number matching (Microsoft, Okta), reduce prompts per session
- Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) Phishing: Phishing sites proxy credentials AND MFA tokens
- Counter: Use FIDO2/WebAuthn hardware keys, educate users to spot fake login screens
- Session Hijacking & Cookie Theft: Stealing authentication cookies, bypasses MFA for the session
- Counter: Deploy short-lived tokens, enable HttpOnly cookies and session anomaly monitoring
- Brute-force on Weak Factors: Automated attacks on SMS/OTP codes with poor lockout rules
- Counter: Remove SMS/email factors, enforce lockouts, use strong methods
- Social Engineering: Scammers trick users into sharing or approving fraudulent MFA events
- Counter: Ongoing user education, enforce call-back/validation procedures
Visual attack guides: See annotated diagrams from Unit 42, PT Security.
2. Enforce Phishing-Resistant, Modern MFA Everywhere
- Hardware Keys & Passkeys (FIDO2/WebAuthn): Set these as required for admin and high-value accounts
- Authenticator Apps (never SMS/email for critical roles): Push notifications with number matching or biometric/USB challenge
- PKI Smart Cards: For regulated/high-security environments
- Regular Review: Quarterly audits of registered factors, logs, unused/legacy accounts
Verification Step:
- Perform a live test: Simulate MFA prompt bombs and phishing attempts; confirm users/admins can spot and DON’T approve unauthorized prompts
- Use platform monitoring (Azure, Okta, Google) to confirm no legacy factors are enabled
3. Harden MFA Policies and Platform Configurations
Microsoft 365 / Entra / Azure AD
- Enable Conditional Access—enforce risk-based MFA
- Require number matching on Authenticator
- Block legacy authentication methods (Basic, SMTP, POP)
- Monitor sign-in logs for anomalous activity and failed MFA attempts
- Full guide: Microsoft 365 MFA Security
Okta
- Enforce adaptive multifactor and behavioral anomaly detection
- Require push with number matching or WebAuthn keys
- Enable session risk monitoring and real-time alerts
- Full guide: Okta Adaptive MFA — refer to Okta's official documentation for details
Google Workspace
- Enforce Security Key–only sign-in (Advanced Protection)
- Enable context-aware access controls
- Monitor activity via Security Center
- Full guide: Google Workspace MFA — refer to Google's official documentation for details
AWS
- Require MFA (hardware or app) for all IAM users and API access
- Shorten session lifetimes; enable CloudTrail and GuardDuty for anomaly detection
- Full guide: AWS MFA
Tip: Print or save reference links for each platform and keep handy for quarterly reviews.
4. Train Users to Spot and Report MFA Bypass Attempts
- Simulate Attacks: Use tools (Hoxhunt, KnowBe4) to run simulated phishing, prompt bombing exercises monthly/quarterly
- Scenario Training: Give examples of phone, email, or login screen scams
- Reporting Protocol: Make it easy for users to escalate suspicious events—dedicated IT/report channels, direct phone lines
- Helpdesk Playbooks: Ensure support teams distinguish legitimate lockouts from targeted attacks
Recommended Materials:
- Download CISA User Training Guide — see CISA's official site for details
- Sample playbooks: Emsisoft Cybersecurity Tips
5. Test and Verify Your Defense—Don’t Trust, Confirm
- Quarterly MFA Simulation: Simulate attacks and check all roles can resist bypass tactics
- Audit Log Review: Confirm no unusual sign-ins, unauthorized approvals, or failed challenge attempts
- Incident Response Drill: Practice step-by-step breach scenarios—can your team identify, contain, and recover?
- Real-World Benchmark: Target >94% reduction in credential-based breaches, as achieved by exemplary MFA deployments (ITRC Breach Report)
6. Troubleshooting & Incident Response: What to Do If MFA Fails
If You Suspect MFA Bypass:
- Lock Down Accounts: Immediately suspend access for affected credentials
- Reset MFA Factors: Re-enroll hardware keys or change passkeys for compromised users
- Audit Recent Sessions: Identify and terminate unauthorized sessions/tokens (Unit 42 IR 2025 Report)
- Report/Escalate: Use official vendor incident forms (Microsoft, Okta) and national agencies (CISA), as appropriate
- Simulate & Review: After containment, run live simulations to shore up weaknesses
Common Error Checkpoints:
- Failing to disable legacy protocols (SMTP, IMAP, POP)
- Relying on SMS/email as a second factor
- Lack of formal user training or alerting protocols
FAQ:
- "Can MFA always prevent breaches?" — No, but phishing-resistant MFA and strong user training stop >94% credential theft (ITRC 2024)
- "Who do I inform in a suspected breach?" — Internal IT/security first, vendor/platform next, then regulators if required
Downloadable Resources & Next Steps
- CISA MFA Policy Template (PDF) — see official CISA site for current downloads
- NIST SP800-63 User Awareness Guide
- Microsoft 365 Incident Response Playbook
- Visual Attack Flow Diagrams (PT Security)
Final Thoughts
MFA is powerful, but only as strong as its configuration and user vigilance. In 2025, continually adapt your defenses, test them, and empower every user. When in doubt—verify, report, and retrain.
For IT leaders: Save this guide, distribute the checklists to staff, and block out time for quarterly MFA stress tests. For business owners and users: Don’t assume “having MFA” is enough—insist on strong, phishing-resistant options and regular awareness training.
Stay safe, stay skeptical, and keep MFA fresh.

