What is AI-Generated Content (AIGC)? Definition, Value, Myths & Practical Insights

One-Sentence Definition
AI-Generated Content (AIGC) is digital content—including text, images, video, audio, and more—created automatically by artificial intelligence models in response to user instructions or prompts, with minimal human intervention.
Detailed Explanation
AIGC leverages generative AI models—such as large language models (LLMs), diffusion models, and neural networks—to create new digital material from user-provided prompts. Unlike traditional automation, AIGC can produce not only structured formats but also dynamic, creative works across multiple modalities (writing, imagery, audio/video, code, etc.). Production typically involves a sequence of steps:
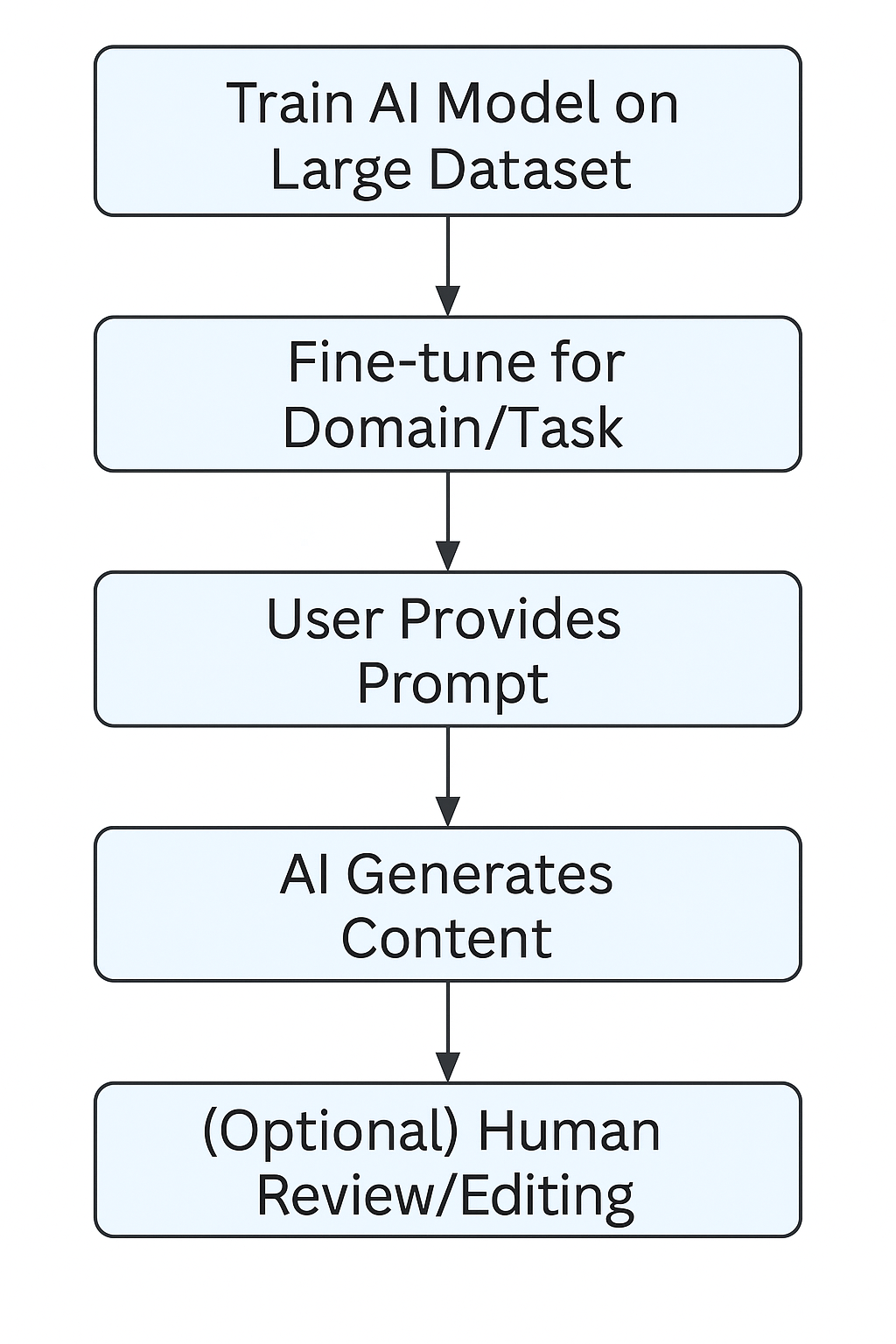
The model is trained on vast datasets of real-world content.
Fine-tuning may adapt the model to specific domains or styles.
Users provide prompts, which guide the generation process.
Human review or editing can be added for quality, compliance, or brand standards.
AIGC now powers everything from blog articles to product images, voice syntheses, automated videos, and beyond. [arXiv:2411.06193v1]
Key Components of AIGC
Generative AI Model: The core engine (e.g., LLM or multimodal model) producing the content.
Training Data: Large, diverse datasets enabling context-aware, relevant outputs.
Prompt Engineering: Crafting effective prompts to optimize quality and relevance.
Human in the Loop: (Optional) Editorial review to ensure accuracy and ethical standards.
Quality & Originality Checks: Detection tools and filters to maintain originality and SEO compliance.
AIGC vs. UGC: Comparison Table
Feature | AIGC (AI-Generated Content) | UGC (User-Generated Content) |
|---|---|---|
Origin | By AI algorithms & prompts | Directly by human users |
Scale | High-volume, scalable | Variable, depends on user participation |
Consistency | High, customizable | Diverse, authentic |
SEO Impact | Can be optimized; risk if low-value/spam | Organic, but unpredictable |
Editorial Review | Optional, can be fully automated | Usually self-edited or lightly moderated |
Typical Use | Blogs, e-commerce, ads, support, media | Forums, reviews, social media posts |
AIGC Content Workflow (Diagram)
Real-World Applications
Content Marketing: Bulk blog/article creation, landing pages, whitepapers
E-commerce: Product descriptions, reviews, ad creatives
Customer Support: Intelligent chatbots, knowledge base content
Social Media: Post and campaign generation, image/video assets
Multilingual Content: Automatic localization/translation
Studies and SaaS case reports note productivity boosts up to 5x for marketing teams—enabling more frequent publishing and increased web traffic within weeks of AIGC adoption.
Myths vs. Facts: SEO, Quality, and Google’s View
Common Myth | The Reality |
|---|---|
AI content is always low quality or generic | With tailored prompts and editorial review, AIGC can be unique, relevant, and engaging |
Google automatically penalizes AI-written text | According to Google Search Central, content is evaluated by quality, relevance, and value—not authorship method. Spammy, low-value AI content can be penalized; well-made AIGC is indexable and can rank well. |
AIGC replaces human creativity | Best outcomes result from combining AIGC speed with human creativity and strategy |
Related Concepts & Further Reading
Generative AI — Core technology behind AIGC
Large Language Model (LLM) — The AI architecture powering content generation
Prompt Engineering — Designing effective AI prompts
User-Generated Content (UGC) — Human-created digital content
SEO Best Practices (Google)
AI-Generated Content transforms how marketers, SMBs, and content creators approach digital publishing: enabling scale, efficiency, and creativity—if used strategically and responsibly.

