Inbox Commerce: What It Is, What It Isn’t, and How It Works Across Email, SMS, RCS, WhatsApp, and Messages for Business
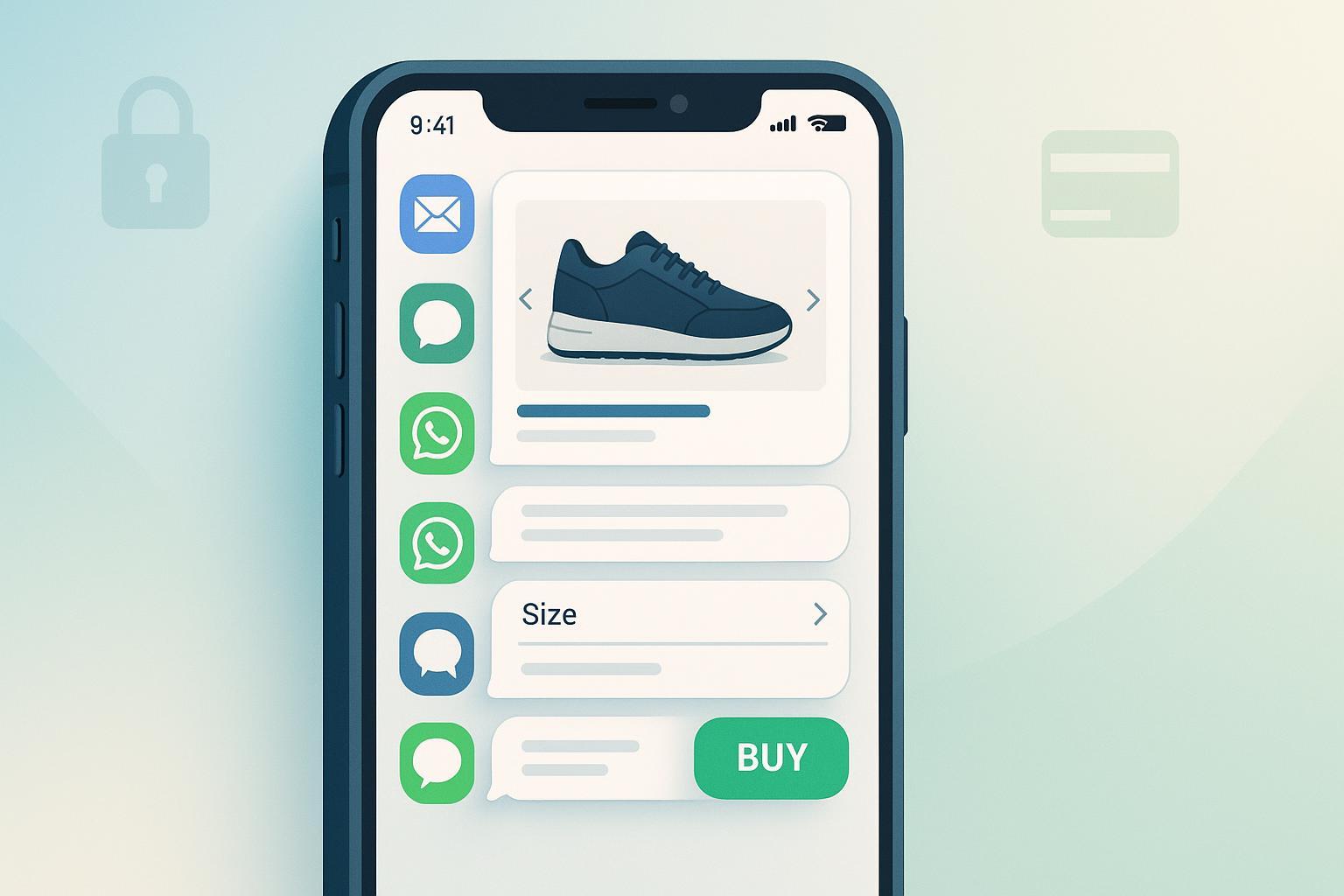
You might wonder: can customers really browse and even buy without ever leaving their inbox? The short answer is “sometimes”—and knowing when and how is exactly what Inbox Commerce is about.
Definition (in plain English)
- Core idea: Inbox Commerce is the practice of enabling shopping and service actions directly inside customers’ messaging inboxes—email, SMS/MMS, RCS, WhatsApp, Apple Messages for Business, and in‑app inboxes—so people can progress from discovery to decision with minimal context switching.
- Expanded: Instead of pushing every click to a website, Inbox Commerce uses native, channel‑specific interactions (carousels, forms, suggested actions, chat flows) and secure handoffs when payment is required. Some channels can complete steps in‑chat (e.g., Apple Pay in Messages for Business, or WhatsApp payments where available), while others primarily capture preferences and then deep‑link to a secure checkout.
What Inbox Commerce is—and isn’t
- It is a way to deliver shoppable, supportable experiences inside inbox channels—reducing friction across the journey (browse → decide → purchase → post‑purchase support).
- It isn’t just “email marketing” or “SMS blasts.” The value comes from interaction design, identity continuity, and secure handoffs—not from sending more messages.
- It isn’t the same as conversational commerce. Conversational commerce emphasizes free‑form chat and agent/chatbot exchanges; Inbox Commerce focuses on the inbox channel’s native UI and policies. They often overlap, but neither subsumes the other.
- It isn’t omnichannel in itself. Inbox Commerce is one orchestration layer within an omnichannel strategy; it does not include social marketplace checkout (e.g., TikTok Shop) or marketplace-native transactions.
The 2025 channel landscape (what’s really possible)
- What works well: Dynamic elements in supported clients (e.g., forms, carousels) let subscribers browse variants, select sizes, answer questions, or submit reviews without leaving the message. These capabilities are defined in the AMP for Email spec from the AMP Project, including components like amp-form and amp-carousel, as documented in the official AMP for Email specification (AMP Project).
- Reality check: AMP interactivity is primarily supported in Gmail and a limited set of clients, so you must include graceful HTML fallbacks. Payment should not be collected in-email; hand off to a secure web/app checkout.
SMS/MMS
- Strengths: Unmatched reach and immediacy; ideal for time-sensitive promos, alerts, and recoveries. Typically relies on short links to prefilled carts or app screens.
- Compliance first: In the U.S., marketing texts generally require prior express written consent under the TCPA; see the governing rule at 47 CFR §64.1200 (eCFR, current). Provide clear sender identification and simple opt‑out (e.g., STOP) and honor it immediately.
RCS (Rich Communication Services)
- What it offers: Rich cards, carousels, suggested replies/actions, and media that support guided discovery and service flows. These capabilities are outlined in Google’s RBM documentation, such as the RBM send messages guide (Google Developers).
- 2025 update: Apple announced RCS support for iOS 18 in 2024, improving cross‑platform messaging with non‑Apple devices, though feature parity still depends on carrier/device rollout; see Apple’s iOS 18 RCS announcement (Apple Newsroom, 2024).
- Checkout reality: Typically a deep‑link handoff to secure web/app. Consider agent handoff for complex questions.
WhatsApp Business Platform
- Interactivity: Meta’s “Flows” enable multi‑screen, structured experiences inside chat (think guided fit, address capture, appointment booking); see WhatsApp Flows introduction (Meta Developer Blog, 2023).
- In‑chat payments (market‑specific): In 2023, Meta announced that people in India can pay businesses within WhatsApp using UPI apps, cards, and more, and that people in Brazil can pay small businesses directly in chat; see WhatsApp payments in India (Meta Newsroom, 2023) and WhatsApp payments in Brazil (Meta Newsroom, 2023).
- Practical note: Outside supported markets, use Flows to reduce friction, then hand off to a secure checkout. Template approvals and conversation-based pricing apply.
Apple Messages for Business
- Capability: Brands can offer support and purchase flows inside Messages, including native Apple Pay sheets for payment where the user and device are eligible. Apple documents these capabilities in its legal and support materials, e.g., Messages for Business & Apple Pay (Apple Legal, accessed 2025).
- Practical note: Requires onboarding and approval. Often shines in service‑to‑sale transitions (returns, exchanges, add‑ons).
In‑app inboxes and web push centers
- Your own app or web notification center can host mini‑threads for nudges, product tips, and support. Payments usually execute via stored cards/passkeys or native pay sheets—still “inbox” in the broad sense because the customer stays in your owned experience.
How checkout really works (and why it matters)
- Most inbox channels are great at discovery, selection, and data capture. Payment steps should be executed either via native in‑chat rails (where supported) or via a secure hosted checkout. Global card data standards such as PCI DSS v4.0 (PCI SSC) require strong protections for cardholder data; do not try to collect card numbers in email or SMS.
- If you sell to the EU/EEA, expect step‑ups like Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) on applicable transactions; the European Banking Authority’s clarifications detail how and when SCA must apply; see EBA SCA clarifications (2023–2024).
Compliance essentials (U.S.-centric with international notes)
- Email: Follow CAN‑SPAM requirements—truthful headers, non‑deceptive subject lines, clear identification, a visible unsubscribe, and prompt opt‑out processing—summarized in the FTC’s CAN‑SPAM guide for business.
- SMS/MMS: Prior express written consent for marketing texts (TCPA), clear identification, and easy opt‑out (STOP). Keep logs and honor quiet hours where applicable; see the TCPA rule at the eCFR citation above.
- WhatsApp/RCS/Apple Messages: Respect platform template rules, review processes, and conversation windows. Don’t treat these channels as “free for all”—policy violations can lead to throttling or suspension.
- Privacy & data: If you process data on EU residents, ensure a lawful basis and respect user rights under GDPR; the European Commission’s portal summarizes key obligations: GDPR overview (European Commission). For Canada, Commercial Electronic Messages fall under CASL; verify consent requirements and unsubscribe mechanics.
Implementation checklist (from zero to first win)
- Identity & trust
- Email: Authenticate with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC; warm your domains and IPs.
- WhatsApp: Complete business verification and secure explicit opt‑in.
- Apple Messages for Business: Apply and complete onboarding; ensure Apple Pay eligibility.
- Content interactivity
- Email: Use AMP where supported with HTML fallbacks; design for graceful degradation.
- WhatsApp/RCS: Use Flows or rich cards with suggested replies/actions; plan agent handoff paths.
- Linking & continuity
- Use deep links with session restore, cart tokens, and passkeys/one‑tap sign‑in to minimize login friction.
- Payments
- Prefer native pay sheets (Apple Pay in Messages for Business; WhatsApp payments where available) or hosted checkouts (Shop Pay, Apple Pay, Google Pay on web/app). Avoid card capture in messages.
- Measurement
- Combine UTMs with server‑side events/postbacks. Use holdout/control groups to measure incremental lift.
- Deliverability & pacing
- Respect platform rate limits, quiet hours, and frequency caps. Monitor deliverability and complaint rates.
Five ready-to-run playbooks
-
Back‑in‑stock alert (Email + SMS)
- Email: AMP block shows size selector; user picks and clicks “Add to cart,” deep‑linking to a prefilled cart.
- SMS: If user didn’t convert within 4–6 hours, send a short follow‑up with a unique short link to the same prefilled cart. Honor opt‑out immediately.
-
Guided fit finder (WhatsApp)
- Use a WhatsApp Flow to ask 3–5 questions about use case, size, and color. Present the top 2 matches with images.
- If the user is in India or Brazil and eligible, present in‑chat payment; otherwise, hand off to a secure checkout page that preserves cart state.
-
Store visit to sale (RCS)
- Send an RCS rich card carousel for a local event or appointment. Include suggested actions: “Reserve,” “Directions,” “Chat with an agent.”
- If the user reserves, follow up with an RCS confirmation and a deep link for payment or pickup instructions.
-
Service-to-sale add‑on (Apple Messages for Business)
- During a support chat (e.g., replacement part), offer a compatible add‑on. If the customer accepts, present an Apple Pay sheet in conversation for instant payment when eligible.
-
Subscription dunning recovery (Email + SMS)
- Email: Notify failed payment; include a secure link to update billing (support passkeys/one‑tap sign‑in).
- SMS: If consented, send a gentle reminder with a unique link. Stop after one follow‑up to prevent fatigue.
Metrics that matter (and how to test them)
- Engagement: delivery rate, open/view rate, tap‑through rate.
- Commerce: conversion from message, checkout completion, AOV, and revenue per message.
- Lifecycle: reorder rate, time‑to‑repeat, churn and dunning recovery.
- Service: CSAT, first‑contact resolution, response latency.
- Testing approach: Always run holdout/control groups to estimate incremental lift. Pair link‑level UTMs with server‑side postbacks so that privacy features and link protection don’t erase your attribution signal.
2025 trends to watch
- Email interactivity remains uneven: AMP for Email works well where supported but needs bulletproof HTML fallbacks.
- RCS becomes more consistent as iOS 18 support rolls out, but feature parity varies by carrier/device and geography; keep SMS fallback paths.
- WhatsApp commerce deepens in select markets via in‑chat payments; elsewhere, Flows plus secure handoff is the pragmatic pattern.
- Apple Messages for Business strengthens the service‑to‑sale bridge where Apple Pay eligibility and onboarding are in place.
Key takeaways
- Inbox Commerce lowers friction by moving key actions into the inbox—then finishing payment safely via native rails or hosted checkout.
- The win comes from channel‑appropriate design, consent and privacy discipline, and rigorous measurement—not from sending more messages.
- Start small with one or two playbooks, build the plumbing for identity and deep links, then scale to more channels as results prove out.
—
Citations and further reading:
- AMP components for email interactivity: AMP for Email specification (AMP Project)
- TCPA SMS marketing rule: 47 CFR §64.1200 (eCFR, current)
- RCS capabilities: RBM send messages guide (Google Developers)
- iOS 18 adds RCS: Apple Newsroom announcement (2024)
- WhatsApp Flows: Meta Developer Blog (2023)
- WhatsApp payments markets: Meta Newsroom India (2023); Meta Newsroom Brazil (2023)
- Apple Messages for Business & Apple Pay: Apple Legal overview
- PCI DSS: PCI DSS v4.0 overview (PCI SSC)
- SCA rules: EBA clarifications on SCA (2023–2024)
- CAN‑SPAM email rules: FTC compliance guide
- GDPR overview: European Commission portal

