GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): An SEO Enhancement for AI Search
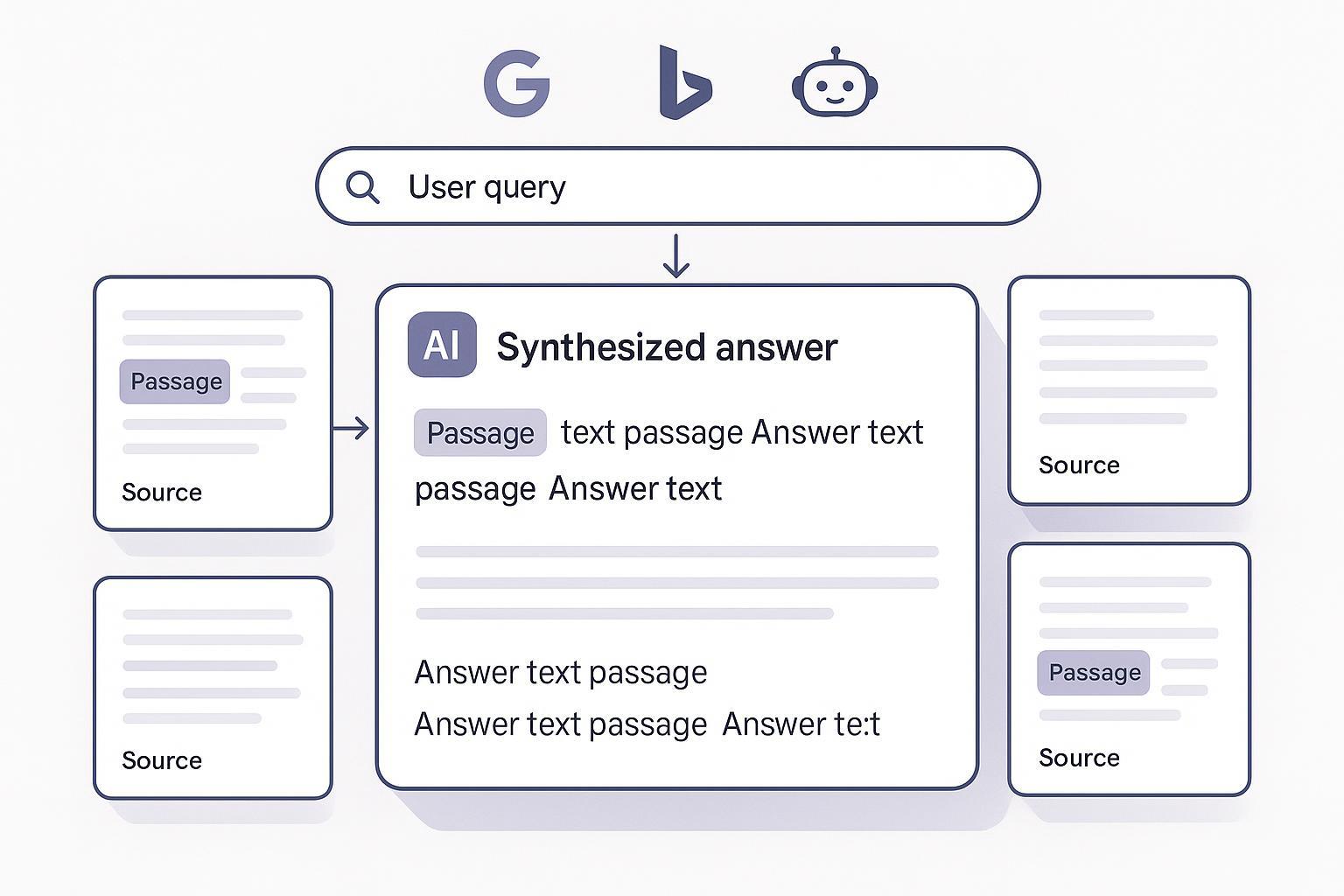
As of 2025, users increasingly get synthesized answers—not just a list of blue links. That shift is why GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, matters. GEO enhances SEO by optimizing your content to be discovered, interpreted, cited, and recommended inside AI-driven search experiences like Google AI Overviews/AI Mode, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and ChatGPT/Gemini. In other words, you still need SEO foundations, but you also need to win where answers are generated.
What is GEO?
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is the practice of shaping your pages so AI answer engines can confidently pull quotable passages, verify them, and include your brand as a cited source in the response. Industry explainers frame GEO as an extension of SEO for AI answers rather than a replacement, emphasizing question-first planning, passage clarity, and evidence transparency. For context, see this accessible overview of GEO’s role in AI search from Search Engine Land (2024), which positions GEO as optimizing for visibility within AI-driven answers rather than just rankings in classic SERPs.
At a high level, most AI answer engines follow a similar pipeline:
Retrieval: find relevant passages across the web (and sometimes from proprietary indexes).
Synthesis: assemble a coherent answer that covers sub-questions and caveats.
Citation: attribute statements to sources for verification.
Google describes AI Overviews/AI Mode as Gemini-powered features that tackle complex queries by fanning out into subtopics, synthesizing an overview, and linking to supporting resources. This is reflected in Google’s 2025 guidance on AI features and helpful content. Microsoft’s Bing Copilot similarly emphasizes retrieval-augmented generation and inline citations that point back to specific passages. Perplexity, by design, attaches citations to every answer to promote source transparency.
Why questions over keywords? Keywords still matter, but questions are the unit of organization for answer engines. If your page directly answers the exact questions people ask—and does so in verifiable, self-contained chunks—it’s far more likely to be quoted. Recent primers (2024–2025) consistently stress this shift from pure keyword targeting to question and intent coverage.
See the definition and scope of GEO in Search Engine Land’s overview (2024).
Explore practical GEO tactics for AI answers in Semrush’s 2025 primer.
For a comparison with traditional SEO, Backlinko/SEO.com provides an updated GEO vs. SEO guide (2025).
GEO vs. SEO: Complementary, not competitive
SEO’s goal: rank URLs in organic listings.
GEO’s goal: get your passages cited and your brand recommended inside generated answers.
They share a lot: E‑E‑A‑T signals (authorship, expertise, citations), topical depth, internal linking, and technical hygiene. But GEO adds new priorities:
Build question hubs around user intents (not just single keywords).
Write passage-first, making key definitions/steps/statistics easy to quote.
Add structured signals (FAQs, how-tos) and clear source citations on-page.
Make authorship, dates, and credentials easy to identify.
If you’ve explored AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) for featured snippets and voice, GEO covers a broader ecosystem across LLM-powered answers. For an accessible breakdown of GEO vs. AEO vs. other acronyms, see Digiday’s “WTF” explainer (2025). For mainstream framing of urgency, Fast Company’s 2025 feature summarizes why brands should prepare for AI-first discovery.
The GEO Playbook (Actionable)
Research user questions
Look beyond tools: review support tickets, sales call notes, and forum threads to uncover real phrasing and objections.
Use search features: People Also Ask, Related Questions, and long-tail query filters in Google Search Console to identify interrogatives.
Sample AI answers: Manually query Perplexity, Bing Copilot, and AI Overviews/AI Mode to see which angles, sub-questions, and sources appear. Track patterns monthly.
Helpful starting points:
Search Engine Journal’s 2025 GEO playbook outlines question research tactics and answer-friendly content patterns.
Search Engine Land’s GSC workflow (2025) shows how to mine long-tail interrogatives from your own data.
Build Question Hubs
Cluster related questions by intent (e.g., “what,” “how,” “should I,” “compare”).
Assign one index page that defines the topic and links to sub-questions.
Cross-link among siblings so AI crawlers and users can navigate the cluster easily.
Include an FAQ section that summarizes the most common Q&As in concise, quotable form.
For B2B SaaS, a “Pricing Models” hub might include “What is usage-based pricing?”, “How to forecast usage spend?”, and “Usage vs. seat pricing: pros/cons.” For retail, a “Fabric Care” hub could cover “How to wash merino wool?”, “Can you tumble dry linen?”, and “How to remove oil stains from cotton?”
Write passage-first Make your key points extractable as 4–6 sentence blocks:
Crisp definition: 1–2 sentences that stand alone.
Steps/checklists: numbered steps, 1–2 lines each.
Pros/cons: symmetrical, factual, concise.
Statistics: include the stat and the named primary source with year.
Comparisons: label criteria (e.g., speed, cost, reliability) clearly.
As industry analyses note, AI engines most often cite declarative, fact-rich, easily extractable content like definitions, how-tos, comparisons, and stats with sources. See Search Engine Journal’s GEO tactics (2025) and Search Engine Land’s answer engine model coverage (2025).
Evidence and E‑E‑A‑T
Put the author name, role, and credentials on the page; link to an author bio.
Add first-publish and last-updated dates near the top.
Cite primary sources with descriptive anchor text (e.g., “In Google’s May 2025 AI Mode update…”). Prefer official docs, standards, or original studies.
Include first-party data when possible (benchmarks, survey results) and explain methodology.
Structured signals and clean formatting
Headings that follow a clear hierarchy (H1 → H2 → H3); one idea per section.
Glossary/definition blocks for key terms on topic pages.
Use FAQPage and HowTo JSON-LD where relevant and validate them.
Example FAQPage snippet (condensed):
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is GEO?",
"acceptedAnswer": {"@type": "Answer","text": "GEO is optimizing content so AI answer engines can cite it in generated results."}
}]
}
</script>
Google’s structured data docs explain how to implement FAQPage and HowTo, and the Rich Results Test validates eligibility. While Google has not published explicit inclusion factors for AI Overviews/AI Mode, clear structure still helps both classic rich results and machine parsing of your page organization.
Technical hygiene that reinforces trust
Ensure fast, mobile-friendly pages; ship a sitemap; set canonical tags correctly.
Use HTTPS, robust caching/CDN, and reliable uptime—slow or flaky sites are less likely to be trusted.
Keep your internal linking logical; use descriptive anchors.
Google’s 2025 documentation on AI features reiterates a “helpful, people-first content” stance and general technical best practices.
A practical GEO toolbox (parity, examples)
Below are neutral examples of tools that can support a GEO-aligned workflow. Choose based on your team’s needs; no single tool is mandatory.
Semrush — Topic research, SERP feature analysis, and content templates; useful for finding question variants and related intents. See Semrush’s 2025 GEO guidance for AI responses.
Clearscope — NLP-driven topical coverage suggestions and content grading to ensure depth and clarity.
Frase — Question research, outline building, and on-page optimization with AI assistance.
QuickCreator — An all-in-one AI content platform that supports question-first outlines, E‑E‑A‑T-oriented quality checks, schema helpers for FAQs/HowTos, and managed technical SEO (CDN, SSL, sitemaps, mobile optimization). Disclosure: QuickCreator is our product. First mention: visit the platform at QuickCreator.
Use tools to accelerate steps you’d do manually anyway: collecting real user questions, structuring coherent hubs, writing quotable passages, and validating markup.
Measurement and feedback loops in a zero‑click reality
Measuring GEO impact means tracking visibility and influence, not just clicks.
AI citation sampling: Build a list of priority queries. Monthly, run them in Google AI Overviews/AI Mode, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity. Log which pages and passages get cited and which competitors appear. Search Engine Land outlines practical ways to monitor a brand across AI channels (2024).
Question-level KPIs: In Google Search Console, filter for interrogatives (who/what/why/how/should). Track impressions and average position even if clicks are flat—these can lead shifts. See SEL’s 2025 GSC research workflow.
Zero-click proxies: Watch branded search volume, direct traffic, and assisted conversions in GA4. Search Engine Journal’s 2025 frameworks discuss presence, perception, and performance metrics for AI-era brand impact.
On-page signal checks: Monitor FAQ clicks, scroll depth to answer blocks, and time-to-first-answer on long guides.
Tie these to business outcomes: Are more users entering through brand queries? Are sales conversations referencing your content they encountered in an AI answer? Those are meaningful wins even when a click didn’t precede the visit.
Myths to drop (and risks to manage)
“GEO replaces SEO.” False. GEO leverages SEO’s foundations—without crawlable, trustworthy content and solid technicals, you won’t be cited.
“Keywords are dead.” No, they still inform intent, structure, and retrieval. Think of keywords as signals that help engines map your content to questions.
“GEO can’t be measured.” You can measure citations, question-level impressions, and business proxies like branded search and assisted conversions, even if some traffic is zero-click.
“It’s just AEO rebranded.” GEO overlaps with AEO but targets a wider ecosystem of LLM-powered answer experiences beyond a single snippet box.
Risks and ethics (as of 2025):
Hallucinations and misstatements: Mitigate by citing primary data, adding dates, and making facts easy to verify. Industry guidance emphasizes transparent, people-first pages for AI SERPs.
Misattribution: Keep facts consistent across your site; use canonical sources and avoid promotional exaggeration that models may downrank.
Ecosystem tension: Zero-click patterns affect publisher economics; litigation and industry debates continue. Marketers should support fair attribution and diversify demand capture.
For timely context on platform directions and industry impacts, see Google’s May 2025 AI Mode update, Bing Copilot’s documentation on retrieval and citation behavior (2025), and mainstream and trade coverage of GEO’s rise throughout 2025.
Future‑proofing: write for passages, vectors, and multimodal answers
Passage-level retrieval is ascendant: Research shows systems often retrieve the best-matching passages, not entire documents. That favors self-contained chunks with clear headings and summary sentences. See Dense Passage Retrieval research (2020) and follow-ons in 2021.
Vector and hybrid search: Modern engines blend semantic retrieval (vectors) with lexical signals (keywords). Optimize for both: align terminology with user phrasing while writing naturally for concepts. For an accessible overview, see Pinecone’s hybrid search explainer (2022).
Multimodal inclusion: Increasingly, answers may show text, tables, and images. Prepare lightweight, labeled assets—summary tables, alt-texted images, and small diagrams that help a model and a user grasp the point quickly.
Practical prep checklist:
Each major page contains: a crisp definition block, a steps/checklist, a short comparison, and at least one stat with a primary source.
Every hub has an FAQ section with 4–6 concise Q&As.
JSON-LD is validated for applicable pages (FAQPage/HowTo); headings mirror user questions.
Assets (images/tables) are compressed, labeled, and described with meaningful alt text and captions.
How QuickCreator fits into a GEO-ready workflow
A pragmatic GEO process looks like this: research user questions, structure question hubs, write quotable passages, add evidence and schema, publish fast pages, and then measure citations and proxy metrics monthly. An all-in-one platform can streamline this.
Question-first outlines and passage structuring to speed drafting.
E‑E‑A‑T-oriented quality checks and on-page reminders (authorship, dates, citations).
FAQ/HowTo schema helpers, glossary-building patterns, and internal linking aids.
Managed technical SEO (CDN, SSL, sitemaps, mobile optimization) for performance and trust.
If you prefer an integrated approach, you can try QuickCreator to assemble a “question hub” and publish GEO‑ready pages in minutes.
Getting started this month (90‑minute plan)
30 minutes: Pull 50 interrogative queries from GSC; add top “People Also Ask” and 10–15 support/sales questions.
30 minutes: Cluster into 3–4 hubs by intent; outline one hub page and 3 sub‑pages with a FAQ.
30 minutes: Draft passage‑first blocks: definition (4–6 sentences), a 5‑step how‑to, a 5‑item pros/cons, and a stat with a primary source link and year. Validate one FAQPage JSON‑LD and publish.
Repeat weekly. In 4–6 weeks, you’ll see question impressions and, ideally, first instances of AI citations.
References and further reading (selected):
Read a clear overview of GEO’s role in AI search in Search Engine Land’s explainer (2024).
Semrush’s primer on tactics to surface in AI answers (2025).
Backlinko/SEO.com’s GEO vs. SEO discussion (2025).
Search Engine Journal’s GEO playbook for AI Overviews/LLMs (2025).
Google’s AI features and helpful-content documentation (2025) and the May 2025 AI Mode update.
Microsoft’s Bing Copilot materials on retrieval-augmented generation and citations (2025).
Perplexity’s description of how citations work in its answers (2025).
Digiday’s 2025 explainer on GEO vs. AEO vs. GSO.
Fast Company’s mainstream 2025 framing of GEO’s urgency.
Dense Passage Retrieval research (2020) and Pinecone’s hybrid search primer (2022).

